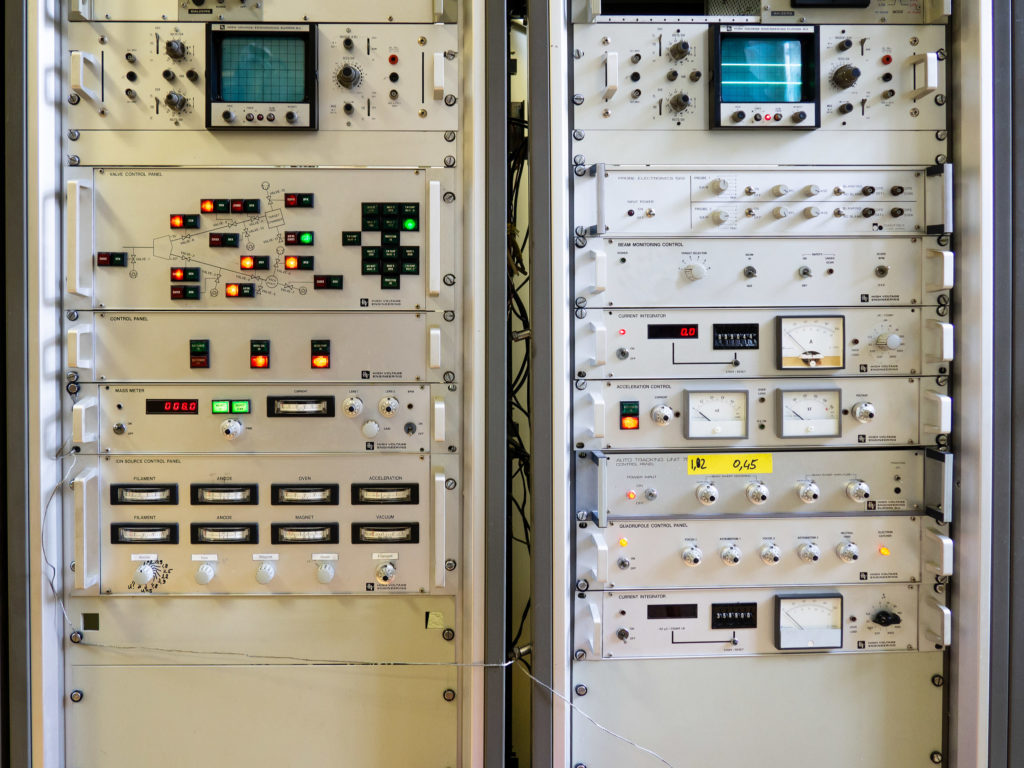
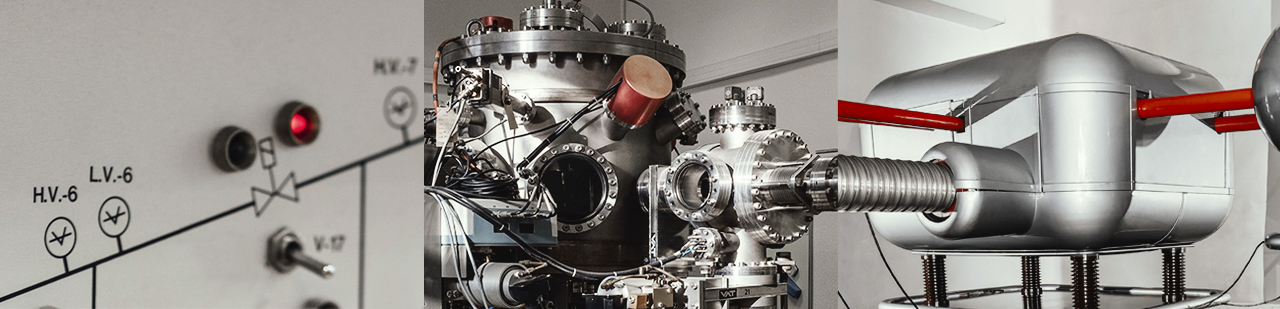
During the ion bombardment of solids, along with the processes of surface sputtering, ion-ion emission, the formation of radiation defects, etc., ions penetrate deep into the bombarded object (target). The most widely used ion implantation is the doping of semiconductors with the goal of creating pn junctions, heterojunctions, and low impedance contacts. Ion implantation in metals is used to increase their hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. Research and experiments on ion implantation are carried out on the HVEE-500 accelerator facility.
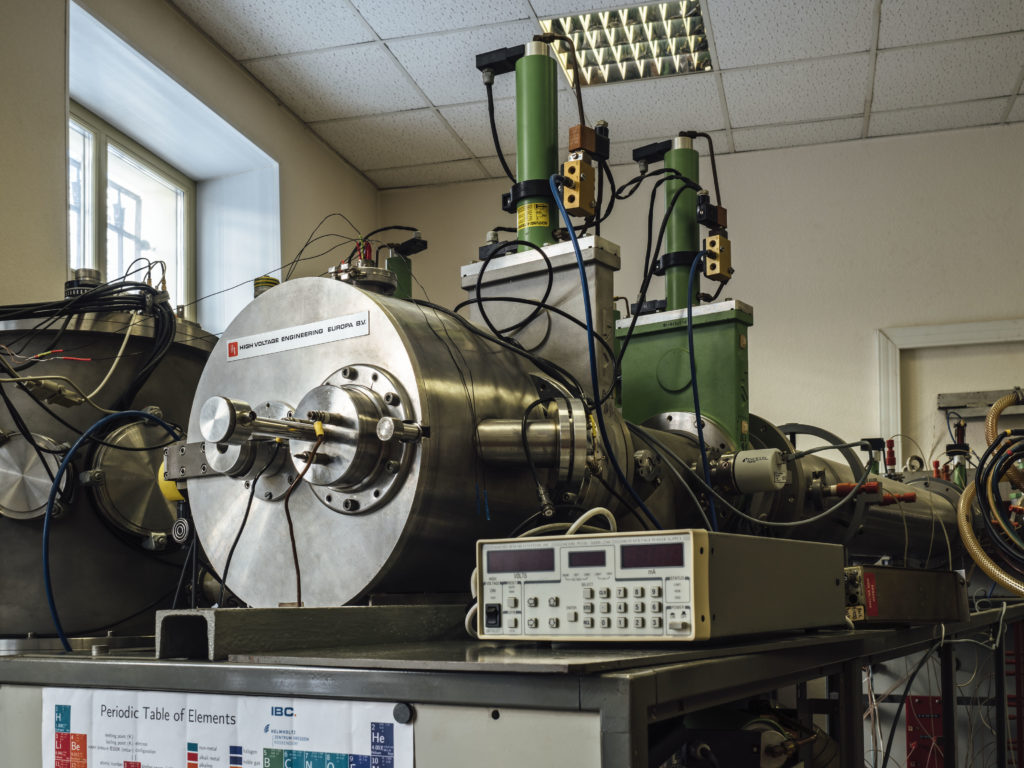
The main characteristics of setup:
- ion energy up to 500 keV for singly charged ions,
- a wide range of ion masses (from 1 to 250 amu),
- high stability of a high voltage source,
- low divergence and small spread in the energies of the ion beam,
- well-separated ion beam, down to isotopes
- diameter of irradiated samples – up to 150 mm.
- substrate temperature: from liquid nitrogen to +600 (an increase is possible)